In a world where social, environmental, and political challenges abound, activism emerges as a potent force driving positive transformation. Rooted in the passion for justice and equality, activism empowers individuals and communities to effect meaningful change by challenging the status quo and advocating for their beliefs. This article explores the multifaceted nature of activism, its historical significance, different forms, and its power to shape the course of society.
Table of Contents
Defining Activism
Activism is the collective and conscious effort of individuals or groups to bring about social, political, economic, or environmental change. At its core, activism is the mobilization of people who are deeply committed to their cause, seeking to create awareness, influence public opinion, and ultimately drive policy changes or social reforms.
Historical Context
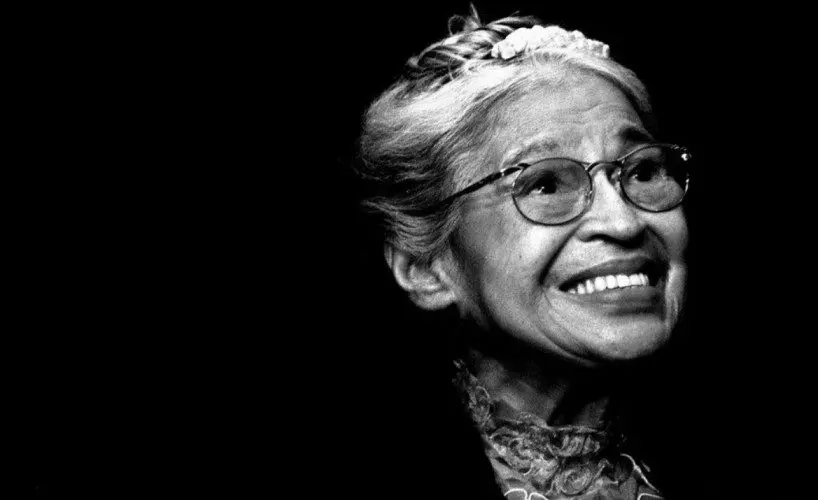
Throughout history, activism has played a pivotal role in shaping societies. From the abolition of slavery to the civil rights movement, activists have stood at the forefront of progress, fighting against oppression and injustice. Pioneers such as Mahatma Gandhi, Martin Luther King Jr., Rosa Parks, and countless others have left indelible marks on the world, inspiring generations to follow in their footsteps.
Forms of Activism
Activism takes on diverse forms, each tailored to the unique needs and circumstances of the cause at hand. Some prominent types of activism include:
a. Protests and Demonstrations: Public gatherings where activists voice their concerns, demand change, and garner attention from the media and policymakers.
b. Civil Disobedience: Non-violent refusal to comply with unjust laws or policies, often drawing attention to the need for reform.
c. Advocacy and Lobbying: Engaging with lawmakers, organizations, and other stakeholders to influence policy decisions.
d. Online Activism: Leveraging social media platforms and the internet to spread awareness, organize campaigns, and raise funds.
e. Environmental Activism: Focused on preserving the environment, combating climate change, and promoting sustainable practices.
f. Human Rights Activism: Committed to protecting and promoting human rights, ensuring dignity and equality for all.
Challenges and Controversies
While activism is a powerful tool for change, it faces various challenges and controversies. Some critics argue that extreme or violent forms of activism can be counterproductive, alienating potential allies and diluting the core message. Moreover, activists may encounter resistance from established power structures, leading to legal challenges, intimidation, or even violence. Striking a balance between conviction and cooperation is essential to foster lasting change.
Impact and Success Stories
Activism has yielded countless success stories that have reshaped the world. From the women’s suffrage movement to the LGBTQ+ rights movement, the power of collective action has led to profound societal changes. Additionally, global initiatives such as the fight against apartheid, the ban on CFCs, and efforts to combat human trafficking demonstrate the global reach and potential of activism.
Contemporary Activism
In the digital age, social media has revolutionized the way activism is conducted. Hashtags, viral campaigns, and online petitions have connected activists across borders, amplifying their voices and influencing international conversations. However, the digital realm also poses challenges like misinformation and echo chambers, which can hinder progress.
Tips for Effective Activism
For those considering engaging in activism, some key principles can help maximize impact:
a. Clarity of Purpose: Define the cause and objectives clearly to inspire and unite supporters.
b. Collaboration: Work with like-minded individuals, organizations, and communities to build a stronger movement.
c. Non-Violence: Embrace non-violent strategies to maintain moral authority and broader support.
d. Inclusivity: Ensure diverse representation to reflect the inclusivity of the movement’s goals.
e. Long-Term Vision: Recognize that change may take time and perseverance is key.
Conclusion
Activism remains a powerful force in shaping the world we live in. Through passion, determination, and solidarity, activists continue to challenge the status quo, push for justice, and create a brighter future for all. As society evolves, so too will the methods and challenges of activism, but its fundamental purpose – to advocate for a better world – will remain unwavering. The call to action stands before us; the question is, will we answer it?